|
 Magnetic
Resonance
Magnetic
Resonance
 CT-Scan
CT-Scan
 Digital
Radiology
Digital
Radiology
 Mammography
Mammography
 Densitometry
Densitometry
 Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
 i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
 @
Swiss
Physicians
email directory @
Swiss
Physicians
email directory
 Tips
page
Tips
page
 Links
Links
Abbreviations
The Hippocratic
Oath
Institute access map
Patient
prepararation
Site map
Home
Website in french
|
Mammography
Full field microdose digital
mammography with computed
assisted diagnosis!
About one quarter of Swiss population
deaths are due to cancer; breast cancer represents half of the
total
number of cancers in women aged more than 40. But it has been
shown
that breast cancer screening after age 50 lowers breast
mortality by
30% to 50%. Screening should take place even earlier if risks
factors
are known, such as family history of cancer.
Screening mammography may reveal non
palpable very small tumours, when only marked by tiny
calcifications or
subtle mammary architecture distortion on a mammogram. At this
stage,
treatment often allows complete cure with minimal sequelae.
Breast self examination: click on the
image  or see Breastcancer.org
explanations
or see Breastcancer.org
explanations
Are included in the breast cancer
screening:
- breast self
examination, which should
be done monthly during one's whole life
- annual careful medical breast
palpation
- screening mammography at least every
two years after age 50, eventually earlier if risk factors
are known.
Mammography is conducted by a
radiologist and consist of three complementary steps:
- patient history (antecedents) looking
for risk factors, nipple discharge, pain, mass or other
symptoms, first
day of last menses, hormone replacement therapy (which
sometimes
induces benign breast changes), operations, etc.
- breast examination, which orientates
mammogram reading
- the mammography itself, consisting of
two roentgenograms of each breast; when done carefully, this
procedure
should not be painful.
Digital
Mammography: this fairly new technique allows image
acquisition
with a selenium convertor without using any film. Advantages
of digital
mammography:
- Brightness and contrast of a digital
image can always be modified, allowing better lesion
detection in dense
breasts
- X-ray dose to the patient is lower
than conventional technique and a view has never to be taken
again
because of overexposition or underexposition. Microdose®
photon
counting technique (Philips) is able to reduce further the
dose by 50%
- Image formation is immediate and
results can be viewed on a screen by the technician and by
the
radiologist
- Computed assisted diagnosis (CAD)
works like a "second look" in helping the radiologist to
detect the
tiniest lesions
- The images may be printed on a film,
on paper, burned on a CD-ROM or sent electronically to the
physician. A
copy is usually retained in the machine for future
comparison.
If palpation and mammograms results are
not conclusive, the radiologist may perform breast ultrasound
for
additional information. A detailed report will be sent to the
physician
in charge of the patient. If the patient is given the films,
she has to
keep them in a safe place and bring them back next time, to
allow
comparative study.
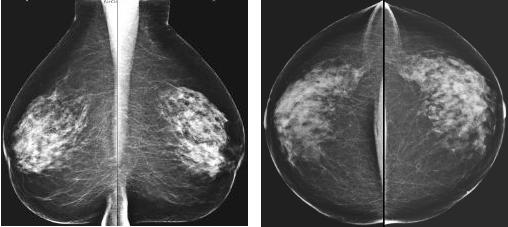
-

Specimen of bilateral mammogram (oblique view)
-
1= breast gland 2= subcutaneous fat 3= pectoralis
muscle
Stereotaxy is
technique using two films of the same breast region obtained
with a
slightly different angle to determine exact puncture location
by
geometrical effect. When a lesion is not palpable, this
procedure
allows precise needle biopsy or placement of a metallic anchor
to
enable surgical removal. Alternatively, ultrasound allows the
same
procedure under direct guidance, especially when breast lesion
contains
no calcifications.

Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) & Breast
Cancer
Estrogen, the major component of HRT helps
relieve menopausal symptoms such as hot flushes. More
importantly, it
is effective in preventing osteoporosis: HRT has been found to
prevent
or slow down bone loss when taken after menopause. It reduces
the risk
of fractures of the hip and spine which can cause serious
disability
and sometimes, even death.
There have been a great number of studies that
have looked at the relationship between estrogen and the risk
of breast
cancer. Within the medical community, it is generally agreed
that HRT
does not increase the risk of developing breast cancer for
women who
have used estrogen for less than 5 years or who take
conjugated
estrogens at doses of 0.625 mg or less. Some studies have
reported that
breast cancer developed more often in women who used estrogens
for long
periods of time (more than 5 years) or who used high doses for
shorter
time periods. On the other hand, there
are
reports stating that current use of HRT may reduce the chance
of breast
cancer detection by mammography. How does HRT interfere with a
mammogram? One of the actions of estrogen is to increase the
density of
breast tissue in some patients. This makes it more difficult
to detect
lumps or small tumors in the breast. The cancer is able to
hide in the
dense breast tissue. Although HRT does not directly cause
breast
cancer, it may affect and lower the efficacy of screening. It
is
therefore recommended that women taking HRT be closely and
properly
followed. In difficult cases, ultrasound is a powerful adjunct
to
diagnosis.

|