![]() Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
![]() i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
@
Swiss
Physicians
email directory
BONE DENSITOMETRY (osteoporosis
diagnosis)

Dual photon energy (DXA) Discovery QDR densitometer
Dual photon energy is scientifically proven as the most accurate technique for bone density measurement. This device allows spine, femur and wrist density measurements, as well as total body composition (fat). A lateral view of the spine may also be obtained for fracture detection, as well as a bone trabecular score (see hereafter).
- Bone calcium loss: a normal process, but sometimes accelerated
- What is my own osteoporosis risk?
- Examination procedure
- Results analysis
- Treatment
- High calcium containing food
From adult age on, bones progressively loose their calcium content throughout life due to excess of urinary waste over assimilation. In women, this loss is stronger after menopause, particularly when menopause occurs early. Other factors are important, such as insufficient exercise, low milk products intake, drugs (prolonged cortisone treatment), family history, etc. Excess bone mineral loss (osteoporosis) may eventually lead to inappropriate and disabling fractures (wrist, spine, femoral neck).
Osteoporosis risk assessment: two tests are proposed hereafter to determine your own risk of osteoporosis:
-The FRAX test (TBS adjusted if available)
- The OST (osteoporosis self-assessment tool) is a simple test for menopaused women, based on age and weight:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40-44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45-49 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50-54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55-59 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60-64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65-69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70-74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75-79 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80-84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85-89 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90-94 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95-99 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interpretation of your results: if your age/weight profile is located in the red or in the yellow zone of the table, or if you have suffered from a low trauma or atraumatic fracture, you should undergo bone densitometry to look for osteoporosis.
B&D.
Uebelhart
Tribune
Médicale 37, 09.2004
Performance of risk indices for identifying low bone density in postmenopausal women.
Mayo Clin Proc. 2002 Jul;77(7):629-37
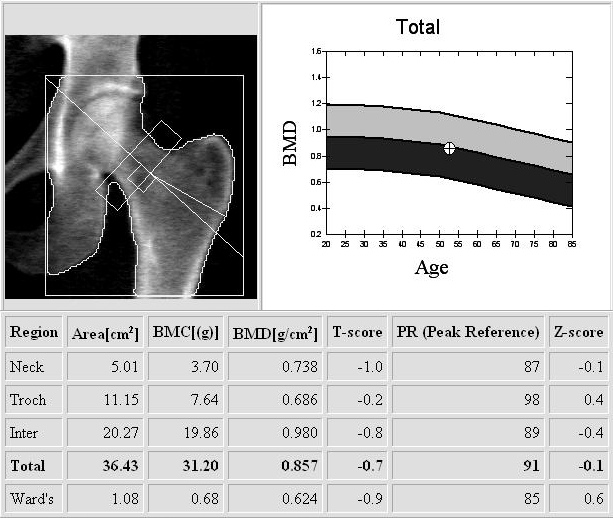
When your physician suspects excessive bone loss (osteoporosis), he may decide to perform bone densitometry which estimates the amount of calcium remaining in bone. You will be lying comfortably on a table for about fifteen minutes. During this time, parts of your body (usually femoral neck and lumbar spine) will be scanned by a thin and very low dose x-ray beam composed of two different wavelengths emitted by an electronic tube; by this way one can subtract on successive locations x-ray absorption values corresponding to bone mineral only from data corresponding to small parts plus bone. Densitometry is safe and painless, but it is of course contraindicated in pregnant women.
|
A density value in g/cm2 is obtained and compared to the mean range of normal values at the same age ad sex; standard deviation (positive or negative) from this range is called z-score; standard deviation from values obtained in young sex matched individuals is called T-score. Osteoporosis as defined by the World Health Organisation is diagnosed when the T-score of the patient exceeds 2.5 negative standard deviations. Beyond this limit fracture risk increases significantly. |
 |
| Image on next right shows a lateral view of the spine obtained with the densitometer. It allows to look for vertebral body deformation, which increases sensitivity for osteoporosis diagnosis and to detect eventual collapsed lumbar vertebral bodies which should be discarded from spine density measurements. |

 |
| Trabeculometry or trabecular bone score (TBS) is a recently approved method for an more accurate bone fragility assessment. The measurement is obtained from the front spine image of the densitometer. The computer determines the bone trabeculae repartition in the vertebrae to obtain a microarchitecture score. TBS is independant of bone density, allowing adjustment of the FRAX and helping treatment planning. Some persons may have, as a matter of fact, normal bone density values and in the same time show deficient bone microarchitecture, which represents an independant fracture risk. | 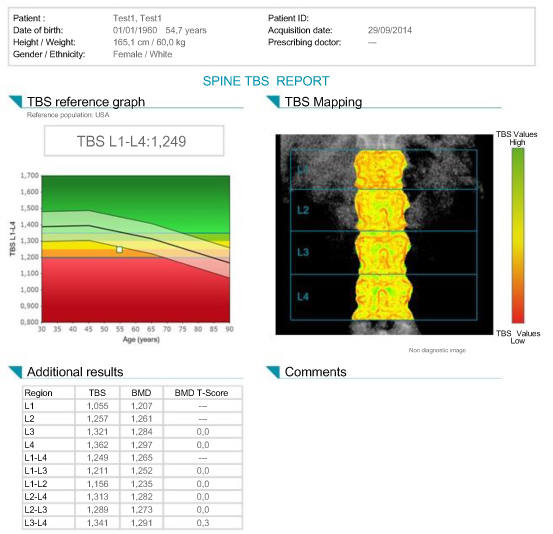 |
Results will be given to your physician, who will prescribe to you if necessary a calcium-rich diet or even drugs in order to increase or at last stabilise your bone mineral content. More exercise and milk products intake are anyway the first step of treatment. Densitometry may be repeated after one or two years to check treatment efficiency. Reliable follow-up measurements should always be done with the same densitometer and in the same institute, because there are slight calibration differences (baseline definition) between different densitometers.
- Dairy products
|
|
|
|
Gruyère, Emmental (hard cheese, "swiss cheese") |
1150 - [55] |
|
Tilsit, Edam |
800 |
|
Melt cheese, soft cheese / Mozzarella |
550 / 400 |
|
Plain milk / Condensed milk |
120 / 230 - [13] |
|
Milk chocolate |
220 - [47] |
|
Yogurt (fat-free) / Buttermilk |
140 / 109 - [14] |
|
White cheese |
90 |
- Fruit and vegetable
|
Sesame |
780 |
|
Hazelnuts / almonds |
250 - [160 / 250] |
|
Beer yeast |
210 |
|
Dried figs |
140 - [62] |
|
Soja tofu / Soja seeds |
130 / 226 |
|
White cabbage / greeen cabbage |
180 / 210 - [43] |
|
Spinach, haricot bean / Endive, broccoli |
120 - [60] / 100 |
|
(Whole bread / Orange) |
(50-90 - [90] / 42) |
- Meat and fish
|
Canned sardines |
400 |
|
Canned salmon |
200 |
|
(other meat and fish) |
(10-40) - [20] |
- Mineral water (mg/100ml)
|
Adelbodner / Eptinger / Denner |
57 / 56 - [130] / 55 |
|
Contrex / Valser |
49 - [80] / 44 |
|
Aproz / Aquella / Salvega |
37 - [70] / 31 / 31 |
|
Lostorfer / Cristella / Coop Prix Garantie / Passugger / San Pellegrino |
28 / 27 / 25 / 21 / 21 - [60] |
|
Rhäzünser / Badoit / Perrier |
20 / 19 / 15 |
|
Cristalp / Henniez / Vichy / M-Budget |
11 / 11 / 10 / 10 - [2] |
|
Vittel / Evian / Arkina / Volvic |
9 / 8 / 4 / 1 |
Daily calcium intake requirements are 1000 mg in adult age, up to 1500 mg in adolescence, pregnancy and nursing, post-menopausal women and older men and women.
Calcium and urolithiasis: "a low intake of calcium can aggravate the risk of stone formation by increasing absorption and urinary excretion of oxalate", which is the main component of urinary stones (Medical Letter, vol.42 april 3 2000, p. 29-30 / Clin Sci (Colch) 1997 Sep 93:257-63 / J Urol 1998 Mar 159:654-7). Patients suffering from renal stones are therefore advised not to restrict their calcium intake in food. Calcium supplements are likewise not considered a risk factor for urinary stones in healthy persons.