![]() Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
![]() i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
@
Swiss
Physicians
email directory
ULTRASOUND AND COLOUR DOPPLER
IMAGING
|

|
Ultrasound imaging or echography is used since early seventies. High frequency inaudible and harmless sounds are emitted through a piezoelectric crystal installed in a probe; contact with skin is ensured by a transmission gel. These sound waves are transmitted at variable speeds through different body tissues. A part of these emitted sounds are reflected by tissue interfaces (acoustic impedance differences) and hit back the probe, which acts simultaneously as a receptor. These signals are computed to form an image visible on the monitor as a slice cut through the examined region. Electronic scanning of the probe many times per second allows dynamic viewing when probe is moved, or observation of spontaneous events inside the body when probe is hold still.
This tool is particularly useful for diagnosis of abdominal diseases (children and adults), foetus survey, neonate brain, small parts (muscle, joints, breast, etc.).
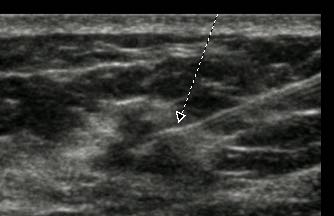
|
|
|
| Ultrasound is also essential to guide punctures, infiltrations and drainages, where ultrasound shows in real time with high precision needle progression through tissues. | CT scan, fluoroscopy and sometimes MRI are also very useful to guide biopsies, drainges and infiltrations. Here is shown a lombar spine infiltration to treat sciatic pain. |
Doppler mode analyses frequency shifts generated when an ultrasound wave reflects on moving particles (red blood cells); the blood flow of arteries and veins is seen on a flow curve (pulsed Doppler) and its speed parameters are analysed to demonstrate stenoses, accelerations, turbulence or obstruction. Colour Doppler allows direct visualisation of flow within vessels with directional colour information, or as an intensity-related colour (Power or Energy Doppler).
Ultrasound
machine with up to date technology, particularly:
multifrequency and soft parts high resolution probes,
harmonics, panoramique view, pulsed
Doppler / colour
Doppler / power Doppler, shear wave elastography.
Artery measurement
of intima-media thickness.

